Data is the most precious asset a company has, from copyrights and client lists to sensitive information about employees. Most data is now in electronic form. It is created and accessed through software, databases, and other tools, making it vulnerable to loss and theft.
- What is data loss prevention? How to take care of your data security
- Main Components of DLP: A small glossary
- Data loss prevention software: why and how to choose
- Questions to ask potential vendors
Let’s start with a real-life experience. When working with an advertising agency, one of my colleagues sent an internal document with all invoices, including prices related to an essential client, to the their account manager’s email address. But unfortunately, instead of choosing the Company/Account she chose the client Company – and the client ended up with a ready-made argument on how to lower their fee. The colleague soon became an ex-colleague, and the client left the agency shortly afterward.
Even though this scenario may seem like an exaggeration, these kind of mistakes happen in every company. Furthermore, they are compounded by malicious intent, such as a disgruntled employee stealing a client’s database to sell to acompetitor, or a contractor downloading a list of every transaction made.
What is Data loss prevention? How to take care of your data security
This approach is not only in the company's business interest, but also legally required by regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA and PCI-DSS. And of course, this process needs to be embedded into company processes and data handling. Every company to some extent, needs to resolve the following issues:
- The protection of intellectual property and trade secrets is vital for your organization's financial results and your brand reputation.
- Regulatory compliance to ensure the compliance with information protection security acts, to detect and prevent regulatory violation.
- Insight into your organization effectivity to optimize internal processes and resources, such as hardware or software use.






The Main Components of DLP: A short glossary
The most important asset is data.
- Data at rest: data stored in archives and databases that is not actively accessed or processed.
- Data at motion: data in transit or in flight that is moved from one location to another, i.e., by copying or downloading. This transfer may happen within an organization network or outside it. Both types need to be protected and are most vulnerable to attack or threat.
- Data in use: active data that is currently being read, processed, updated or deleted by the system.
- Data loss: event that results in data being deleted, corrupted, or made unavailable
- Data leakage/data leaks: unauthorised transmission of data
- Data breach: intentional or unintentional release of sensitive information
These data issues can happen at endpoints, like on devices such as computers, mobile phones, tablets, or printers and USBs, or on shared folders, NAS, or servers. Endpoint security is a critical part of data protection in times of hybrid work and BYOD.

- Data identification and classification simply means discovering where the data is and if it needs to be protected, and to what extent. This process may be manual, using rules and metadata, or semi-automatic using content & context classification and end-user classification. In the future, AI and ML could theoretically enable fully automated classification (but should still be subject to human control). Data classification is done using content and context.
- Content of the data: if a document contains credit card numbers or hospital patient information, it would be worth preventing it from being sent to persons outside the company or even unauthorized persons within an institution.
- Context of the data: where and when the information was created, where was it stored, and how it was changed.
- And finally, with all these components in place, you may be able to detect data leaks and/or prevent them. Detection means having the information after the fact (such as an alert that an employee sent a sensitive file outside the company). In contrast, prevention means making sure a leak doesn't happen (e.g., when attempting to upload a file to the internet, the upload is blocked).
Data loss is caused by internal and external actors.

Data loss prevention software: why and how to choose
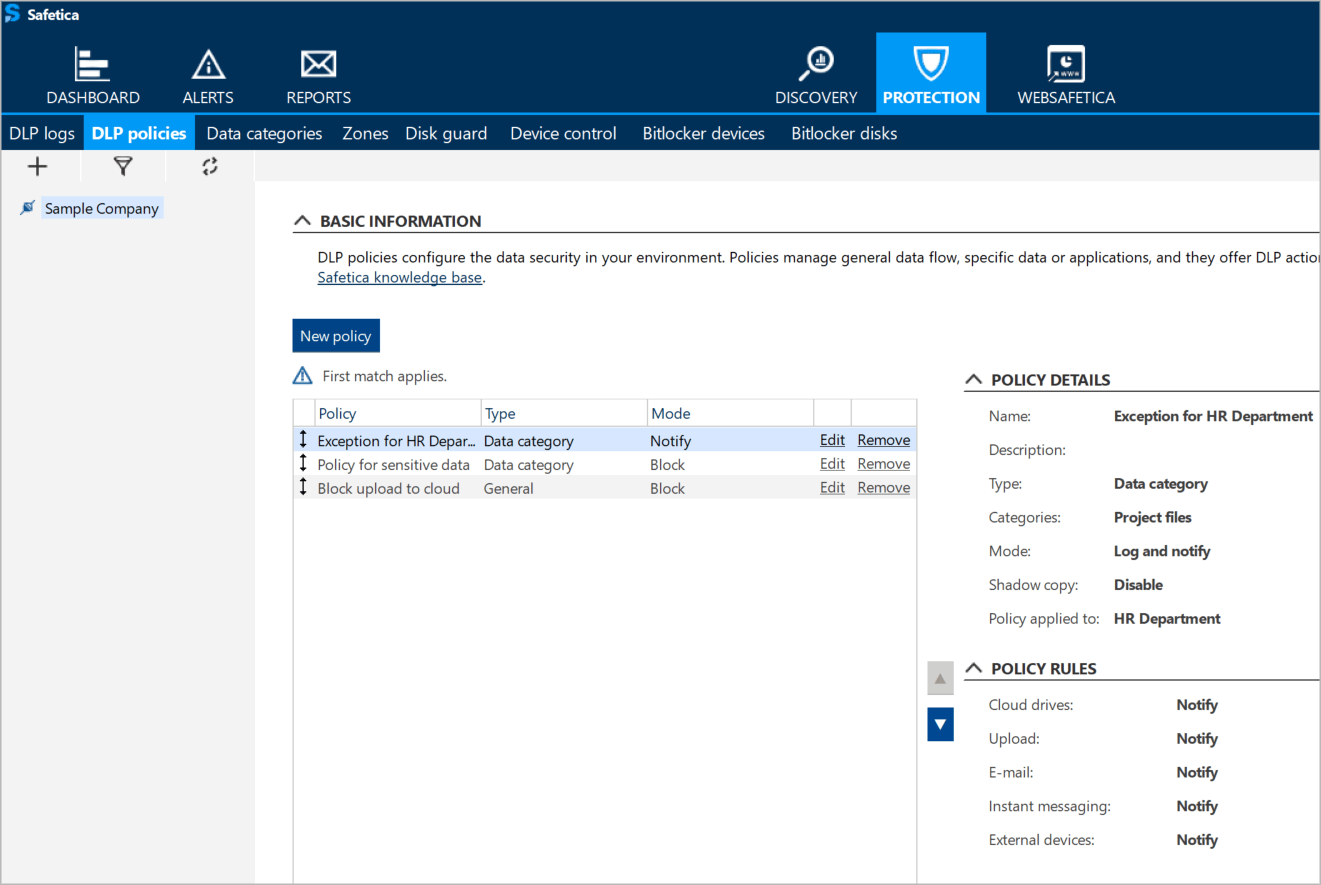



How to choose a DLP solution? First, you need to determine what legal frameworks apply to your company and what main scenarios you want to protect: audit and monitor your data, protect your data against insider threat or audit your company's use of resources.
Questions to ask potential vendors
- Does it cover the security scenarios of your organization?
- Is it sufficient for the size and complexity of your organization?
While the end-user of DLP software is often a single technician, the information gathered offers essential information concerning company-wide issues, such as the rise in data incidents, a sudden surge of insider threat, or sub-optimal use of company resources.
If you want your platform not only to deliver protection and prevention when it comes to data security but also offer you valuable insights, incorporate them into your reporting stack and make it part of your data-driven management.
Your data is your most important asset – protect it accordingly.
Choosing and implementing DLP software are integral parts of a company-wide initiative for general data management and protection. Just as it is normal for a company to protect its data against external attacks by using antimalware and firewalls, antimalware, and secure web gateways, it should also be natural to use DLP software to protect the data against loss and insider threat.
Why Safetica
Learn how can Safetica meet company sensitive data protection and operation audit goals.
Next articles
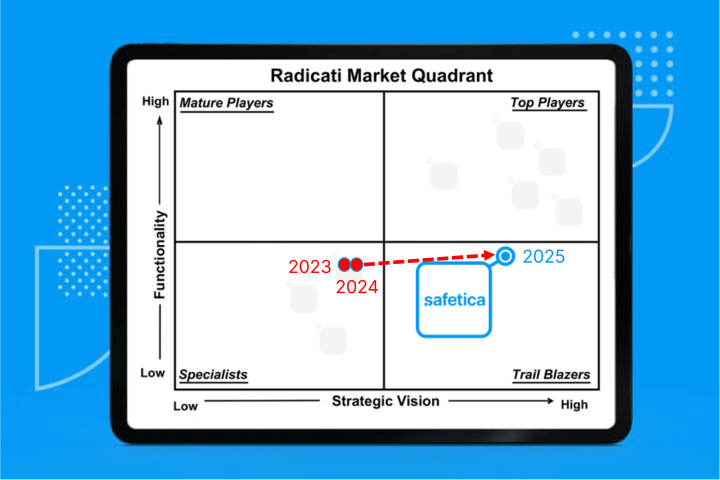
Safetica recognized as a Trail Blazer in Radicati’s 2025 Data Loss Prevention Market Quadrant
The release of Intelligent Data Security positions Safetica as a leader in Strategic Vision

